Google just made sideloading Android Wear apps harder

Android Wear smartwatches are an extremely common breed of wearables. Being full of features and comparatively cheap, it is increasingly common to spot them on people's wrists. While the OS is far from flawless, partly due to the heavy Java-based software stack, bringing to usually lower the standby time than most proprietary competitors, and partly due to the somewhat lacking user experience, these devices have been very popular among developers, since porting Android applications to watches has been made overall easy by the many shared libraries and SDKs.
However, if the OS has been so far relatively open to custom applications, in the last days Google seemed to take some steps on Apple's route, preventing the already enable-only option to "sideload" applications coming from outside the Google Play Store on these devices. As Android Police reports:
According to an email Google is sending out to Wear OS developers, sideloading apps that aren't available on the Play Store is about to get a lot more complicated starting March 10. You'll no longer be able to sideload apps from your phone via the Play Store -> Apps on your phone section on watches, making it next to impossible to add unapproved apps to your watch without turning to tools meant for developers, like the Android Debug Bridge (ADB).
In other words, it will need experienced users (or some custom GUI for this ADB task) to sideload applications, and it is still unknown how far Google will follow this approach. Locking the OS entirely from of signed developer apps would be surprising.
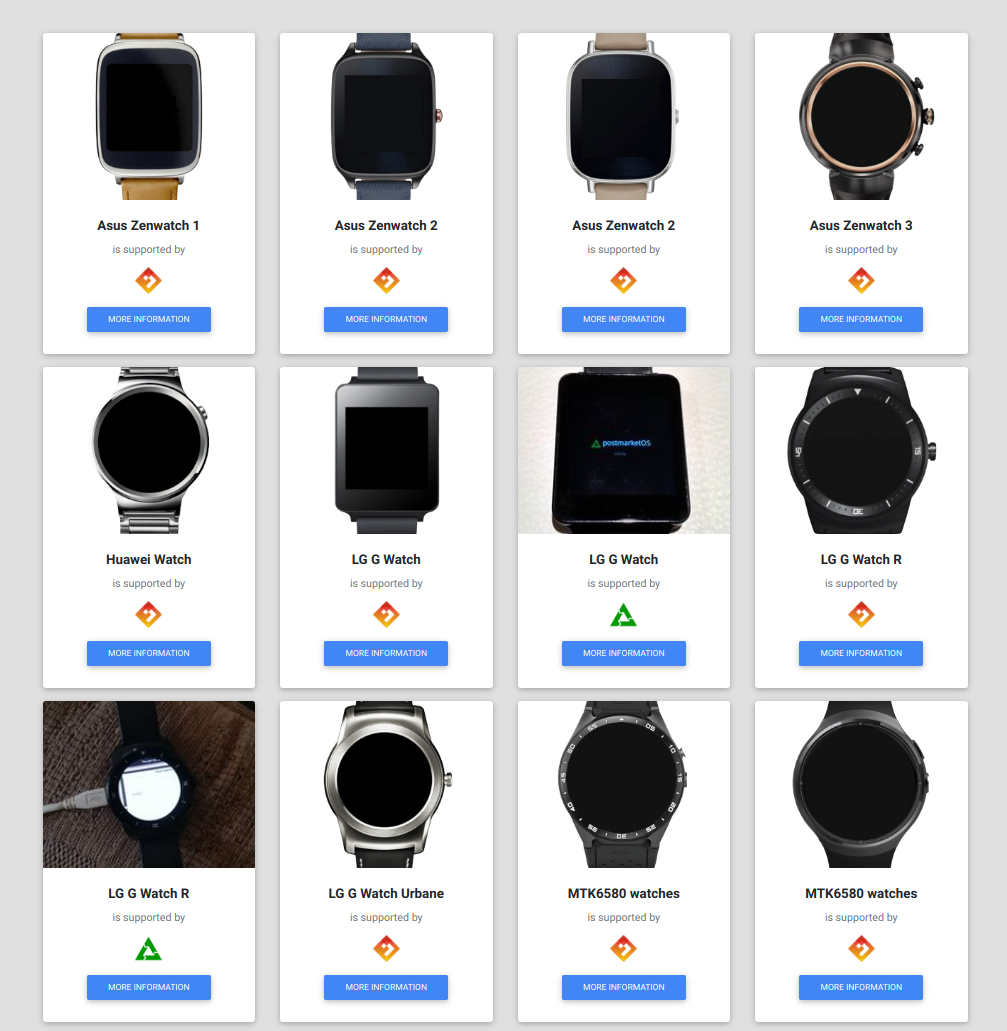
While Android watches tend to follow the same curve of obsolescence of hardware-equivalent phones, open source projects like the AsteroidOS lightweight Linux UI are specifically designed to extend the lifespan of these devices. PostmarketOS also supports a small fraction of the consumer watch market, although no watch-friendly UIs are available in it yet. In fact, AsteroidOS even offers a companion app (Telescope) for Ubuntu Touch smartwatches, closing the gap between these two kinds of Linux mobile devices.
The good news is, several Android Wear devices are based on phone-like Qualcomm (2xx or 4xx) or Mediatek chips and support bootloader unlocking. The exceptions to this rule usually belong to the several "fashion" Wear watches (e.g. some models from Skagen, Fossil, Louis Vuitton, Michael Kors etc.) which do not have any hardware pins for obtaining a debug shell. Some other watches do, but without offering any possibilities of bootloader unlocking.
Initial support of AsteroidOS for the Ticwatch E & S. Contributions welcome! pic.twitter.com/94ZaOj8dzm
— AsteroidOS (@AsteroidOS) May 4, 2019
Via: Android Police, Twitter/Liliputing




Comments ()